
Jūs turite būti prisijungę
Category


Nuotraukos yra skirtos tik informaciniams tikslams. Peržiūrėkite produkto specifikaciją
please use latin characters
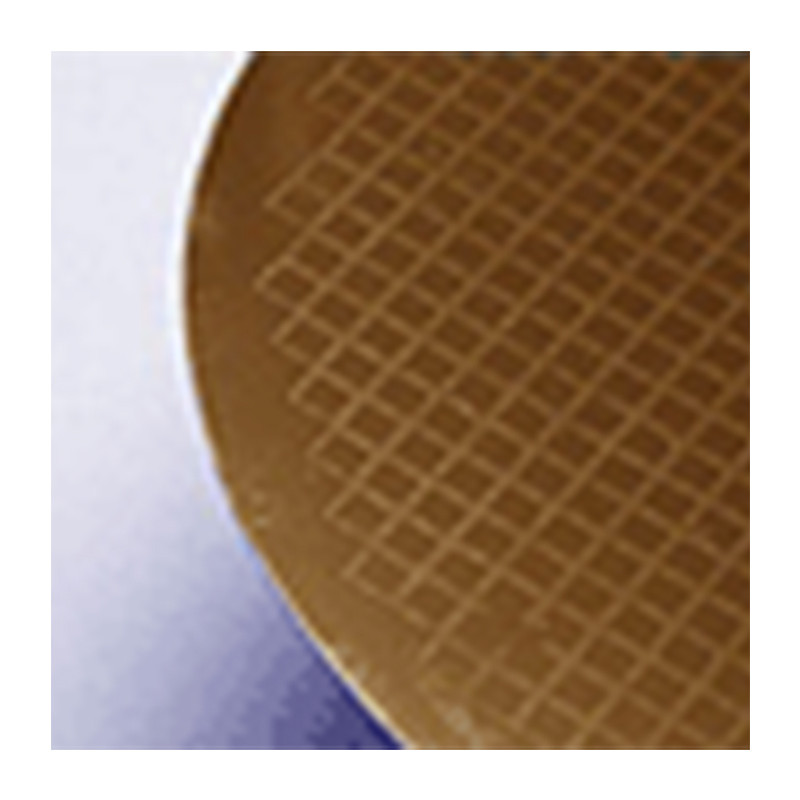
Metal Oxide/Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition, also referred to as gas plating, involves passing metal oxides across a work piece in an inert gas to deposit a layer of metal oxide on the surface. MOCVD is largely utilized by the semiconductor industry. The base wafer - silicon or germanium - must be heated on a graphite susceptor to a very high temperature in order to accept the deposition. First, propylene is passed over the wafer to clear the carbon. Then, a semiconductor material is produced by doping the silicon wafer with either Aluminum to form a p-type semiconductor or Boron for an n-type. The MOCVD process offers good material distribution capabilities and reproduces fine details with reliable quality. The materials to be coated must be able to withstand the extreme temperatures associated with this process.
Modern induction heating provides reliable, repeatable, non-contact and energy-efficient heat in a minimal amount of time. In some material testing experiments, heat must be applied in a very controlled and accurate manner. Induction heating can provide this precision at a wide range of speeds and temperatures, while also accommodating temperature input devices to control temperature ramp and patterns. Thermocouples are often used to measure temperature, with a temperature controller in direct communication with the power supply.
Ameritherm's solid state power supplies are rated for a 100% duty cycle, which is ideal for long term or long cycle testing. Specially designed induction heating coils have been developed to provide uniform heating over the length of a testing specimen.
Induction systems typically used for material testing range from 1 to 20 kW, depending on the material and application requirements.
Ar Jūs domina šis produktas? Ar Jums reikia papildomos informacijos ar individualaus pasiūlymo?
tu turi būti prisijungęs
Metal Oxide/Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition, also referred to as gas plating, involves passing metal oxides across a work piece in an inert gas to deposit a layer of metal oxide on the surface. MOCVD is largely utilized by the semiconductor industry. The base wafer - silicon or germanium - must be heated on a graphite susceptor to a very high temperature in order to accept the deposition. First, propylene is passed over the wafer to clear the carbon. Then, a semiconductor material is produced by doping the silicon wafer with either Aluminum to form a p-type semiconductor or Boron for an n-type. The MOCVD process offers good material distribution capabilities and reproduces fine details with reliable quality. The materials to be coated must be able to withstand the extreme temperatures associated with this process.
Modern induction heating provides reliable, repeatable, non-contact and energy-efficient heat in a minimal amount of time. In some material testing experiments, heat must be applied in a very controlled and accurate manner. Induction heating can provide this precision at a wide range of speeds and temperatures, while also accommodating temperature input devices to control temperature ramp and patterns. Thermocouples are often used to measure temperature, with a temperature controller in direct communication with the power supply.
Ameritherm's solid state power supplies are rated for a 100% duty cycle, which is ideal for long term or long cycle testing. Specially designed induction heating coils have been developed to provide uniform heating over the length of a testing specimen.
Induction systems typically used for material testing range from 1 to 20 kW, depending on the material and application requirements.
Jūsų atsiliepimo įvertinimas negali būti išsiųstas
Pranešti apie komentarą
Pranešimas apie atsiliepimą išsiųstas
Jūsų pranešimas apie atsiliepimą neišsiųstas
Parašyti savo atsiliepimą
Atsiliepimas išsiųstas
Jūsų atsiliepimas neišsiųstas
