trebuie să fii logat
-
întoarce-teX
-
Componente
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductoare
- Diode
- tiristoare
- Module izolate electric
- Redresoare în punte
-
Tranzistoare
- tranzistoare GeneSiC
- Module MOSFET Mitsubishi SiC
- Module MOSFET STARPOWER SiC
- Module MOSFET ABB SiC
- Module IGBT de la MITSUBISHI
- Module de tranzistori MITSUBISHI
- module MITSUBISHI MOSFET
- Module de tranzistori ABB
- Module IGBT de la POWEREX
- Module IGBT - de la INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Elemente semiconductoare din carbură de siliciu
- Accesați subcategoria
- Șoferii
- Blocuri de putere
- Accesați subcategoria
- Traductoare de curent și tensiune LEM
-
Componente pasive (condensatori, rezistențe, siguranțe, filtre)
- Rezistoare
-
Siguranțe
- Siguranțe miniaturale pentru sisteme electronice din seria ABC și AGC
- Siguranțe tubulare cu acțiune rapidă
- Inserții întârziate cu caracteristici GL/GG și AM
- Legături sigure ultra-rapide
- Siguranțe standard britanice și americane cu acțiune rapidă
- Siguranțe cu acțiune rapidă standard european
- Siguranțe de tracțiune
- Siguranțe de înaltă tensiune
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Condensatoare
- Condensatoare pentru motoare
- Condensatoare electrolitice
- Condensatori Icel Film
- Condensatoare de putere
- Condensatoare pentru circuite DC
- Condensatoare de compensare a puterii
- Condensatoare de înaltă tensiune
- Condensatoare pentru încălzire prin inducție
- Condensatoare de impulsuri
- Condensatoare DC LINK
- Condensatoare pentru circuite AC/DC
- Accesați subcategoria
- Filtre anti-interferențe
- Supercondensatoare
- Protecție la supratensiune
- Filtre de emisii revelatoare TEMPEST
-
Descărcător de supratensiune
- Descărcătoare de supratensiune pentru rețeaua de curent alternativ
- Descărcătoare de supratensiune pentru rețea de curent continuu
- Limitatoare de joasă tensiune ALVL
- Limitatoare de joasă tensiune PG
- Descărcătoare de trăsnet pentru rețele de curent alternativ până la 1000V
- Dispozitive de măsurare
- Accesați subcategoria
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Relee și Contactoare
- Teoria releelor și contactoarelor
- Relee cu stare solidă trifazată CA
- Relee cu stare solidă DC
- Regulatoare, sisteme de control și accesorii
- Porniri ușoare și contactoare inversoare
- Relee electromecanice
- Contactoare
- Comutatoare rotative
-
Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate
- Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate Seria 1 | D2425 | D2450
- Relee semifazate CA monofazate, seria CWA și CWD
- Relee semifazate CA monofazate seriile CMRA și CMRD
- Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate Seria PS
- Relee cu stare solidă AC seria duble și cvadruple D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D
- Relee monofazate din seria GN
- Relee cu stare solidă CA monofazate Seria CKR
- Relee monofazate pentru șină DIN AC SERIA ERDA și ERAA
- Relee AC monofazate pentru curent de 150A
- Relee duble cu stare solidă integrate cu radiator pe șină DIN
- Accesați subcategoria
- Relee cu stare solidă imprimabile monofazate CA
- Relee de interfață
- Accesați subcategoria
- Miezuri și alte componente inductive
- Radiatoare, Varistoare, Protectie termica
- Fani
- Aer conditionat, Accesorii tablou, Racitoare
-
Baterii, încărcătoare, surse de alimentare tampon și convertoare
- Baterii, încărcătoare - descriere teoretică
- Baterii litiu-ion. Baterii personalizate. Sistem de management al bateriei (BMS)
- baterii
- Incarcatoare de baterii si accesorii
- UPS și surse de alimentare tampon
- Convertoare si accesorii pentru fotovoltaice
- Stocarea energiei
- Pile de combustibil cu hidrogen
- Celule litiu-ion
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Automatizare
- Elevatoare Spiralift
- Piese pentru drone Futaba
- Întrerupătoare de limită, Micro întrerupătoare
- Senzori, traductoare
- Pirometre
- Contoare, relee de timp, contoare de panou
- Echipament industrial de protectie
- Semnale luminoase și sonore
- Cameră termică
- Afișaje LED
- Butoane și întrerupătoare
- Accesați subcategoria
-
Cabluri, fire Litz, Conduite, Conexiuni flexibile
- Firele
- Presetupe și manșoane
- Chipurile
-
Cabluri pentru aplicatii speciale
- Cabluri de prelungire și compensare
- Cabluri de termocuplu
- Cabluri de conectare pentru senzori PT
- Cabluri cu mai multe fire de temperatură. -60°C până la +1400°C
- Cabluri de medie tensiune SILICOUL
- Cabluri de aprindere
- Cabluri de incalzire
- Cabluri cu un singur conductor temp. -60°C până la +450°C
- Fire de cale ferată
- Cabluri de încălzire în ex
- Cabluri pentru industria de apărare
- Accesați subcategoria
- tricouri
-
Impletituri
- Impletituri plate
- Impletituri rotunde
- Impletituri foarte flexibile - plate
- Impletituri foarte flexibile - rotunde
- Impletituri cilindrice de cupru
- Impletituri si capace cilindrice din cupru
- Curele flexibile de împământare
- Impletituri cilindrice din otel zincat si inoxidabil
- Impletituri de cupru izolate PVC - temperatura de pana la 85 de grade C
- Impletituri plate din aluminiu
- Kit de conectare - impletituri si tuburi
- Accesați subcategoria
- Echipament de tracțiune
- Capse de cablu
- Sine flexibile izolate
- Sine flexibile multistrat
- Sisteme de management al cablurilor
- Accesați subcategoria
- Vezi toate categoriile
-
Semiconductoare
-
-
- Furnizori
-
Aplicații
- Automatizare HVAC
- Automatizare industrială
- Băncile de energie
- Cercetare si masuratori de laborator
- Componente pentru zonele cu pericol de explozie (EX)
- Echipament industrial de protectie
- Echipamente pentru dulapuri de distributie si control
- Exploatare minieră, metalurgie și turnătorie
- Imprimare
- Încălzire prin inducție
- Inginerie energetică
- Mașini CNC
- Masini de sudura si sudori
- Mașini de uscare și prelucrare a lemnului
- Masini pentru termoformarea materialelor plastice
- Măsurarea și reglarea temperaturii
- Motoare si transformatoare
- Surse de alimentare (UPS) și sisteme redresoare
- Tracțiune cu tramvai și feroviar
- Unități DC și AC (invertoare)
-
Instalare
-
-
Inductori
-
-
Dispozitive de inducție
-
-
Serviciu
-
- Kontakt
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
New 800A/1200V Full SiC Module

New 800A/1200V Full SiC Module
By using SiC-based semiconductors the performance of power electronic systems can be drastically improved.
By Eckhard Thal, Koichi Masuda and Eugen Wiesner, Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V., Ratingen, Germany
The evolution of SiC technology in power modules and its principle loss reduction potential are shown in Figure 1. Mitsubishi has developed two new full SiC module types with 800A and 1200A rated currents and 1200V rated voltage [1]; [2]. This article is describing the 800A module.
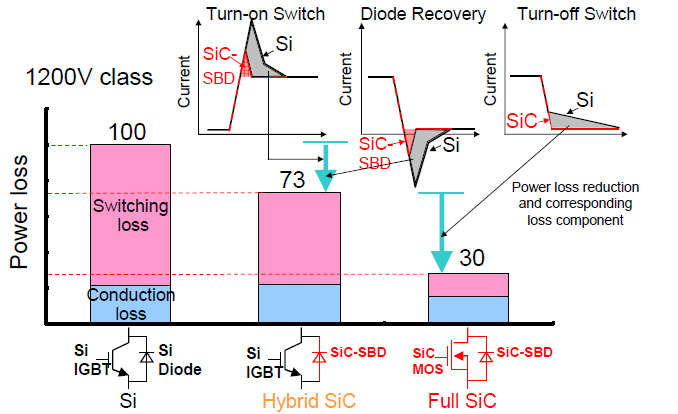
Figure 1: Evolution of SiC technology in power modules
Package outline and circuit diagram
The appearance of new 800A/1200V full SiC module (type name: FMF800DX-24A) and its internal circuit diagram are shown in Figure 2. The module contains 2 x 400A half bridge configurations. By externally paralleling the main P-, N- and AC-terminals an 800A/1200V 2in1 configuration is formed. By this paralleling approach the internal package inductance LS has been decreased to less than 10nH, which is important for limiting the overvoltage spikes at chip level due to high di/dt at switching of SiC-MOSFET.
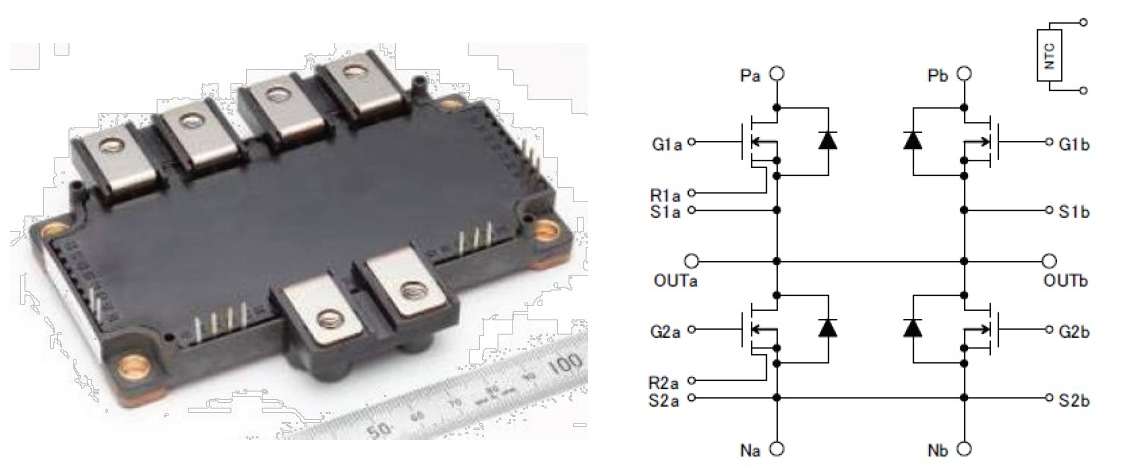
Figure 2: FMF800DX-24A package outline and internal circuit
The baseplate dimension of FMF800DX-24A is 62mm x 121mm. Thus the module size of new 800A/1200V full SiC module is about 1/2 compared with conventional Si-based IGBT modules having the same current rating, see Figure 3.
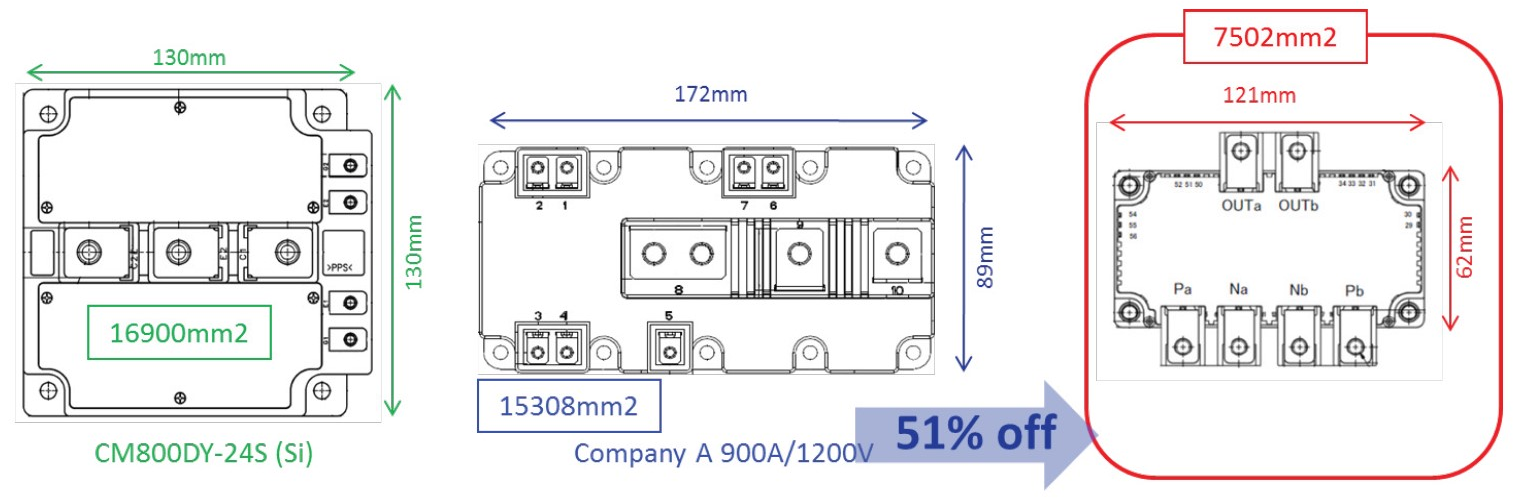
Figure 3: Footprint comparison
For monitoring the baseplate temperature TC a NTC-sensor located close to the MOSFET/FWDi chips is incorporated into the module. For short circuit and overcurrent protection MOSFET-chips with on-chip current sensing are used in one of the half bridge configurations (see Figure 2).
Main module parameters
The main parameters of 800A full SiC module are shown in Table 1.
The values of VDS, RDS(on) and VSD are given on chip level.
| Symbol | Parameter | FMF800DX-24A |
|---|---|---|
| VDSX | Drain-source voltage (at VGS=-15V) | 1200V (max) |
| ID | Drain current | 800A |
| ID(max) | Max. drain current (pulse) | 1600A |
| TJ(max) | Max. junction temperature | 150°C |
| VDS(on) | Drain-source On-voltage @ ID; TJ=150°C | 2,4V (typ) |
| RDS(on) | Drain-source On-resistance @ ID; TJ=150°C | 3,0mΩ (typ) |
| VSD | Source-drain voltage @ -ID; TJ=150°C | 2,2V (typ) |
| VGS(+) | Gate-source On-voltage | 13,5V…16,5V |
| VGS(-) | Gate-source Off-voltage | -9V…-16,5V |
| Rth(j-c)Q | MOSFET thermal resistance | 42 K/kW |
| Rth(j-c)D | FWDi thermal resistance | 61 K/kW |
Table 1: Main FMF800DX-24A parameters
Switching characteristics
Typical turn-on and turn-off switching waveforms at VCC=800V; TJ=150°C; RG(on)=RG(off)=5Ω are shown in Figure 4 and 5 for different drain currents ID=140A…1400A.
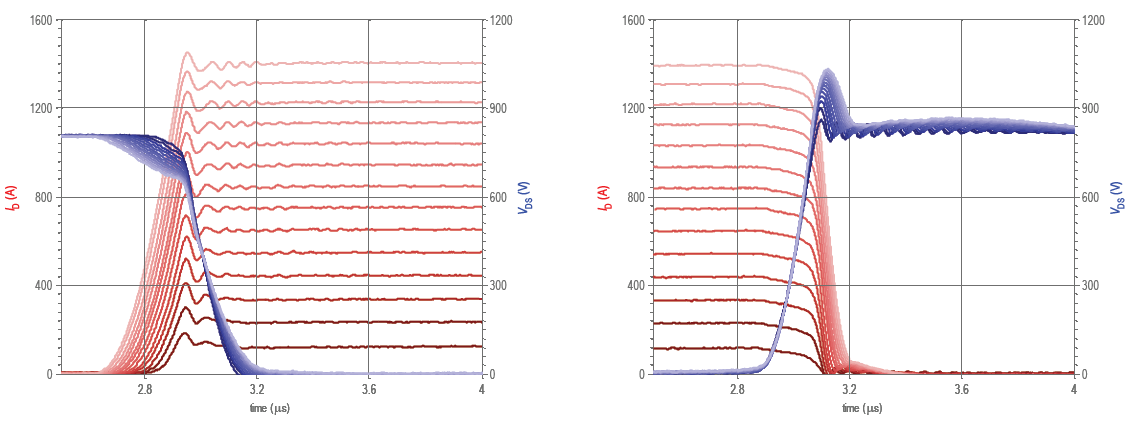
Figure 4: Turn-on waveforms / Figure 5: Turn-off waveforms
For limiting the turn-off overvoltage spike a cross-snubber capacitor of CS=6μF was connected between P- an N-terminals. The dependency of switching speed di/dt on drain current ID is shown in Figure 6 and 7 for different junction temperatures TJ=25°C; 75°C; 125°C; 150°C and different DC-link voltages VCC=600V; 800V.
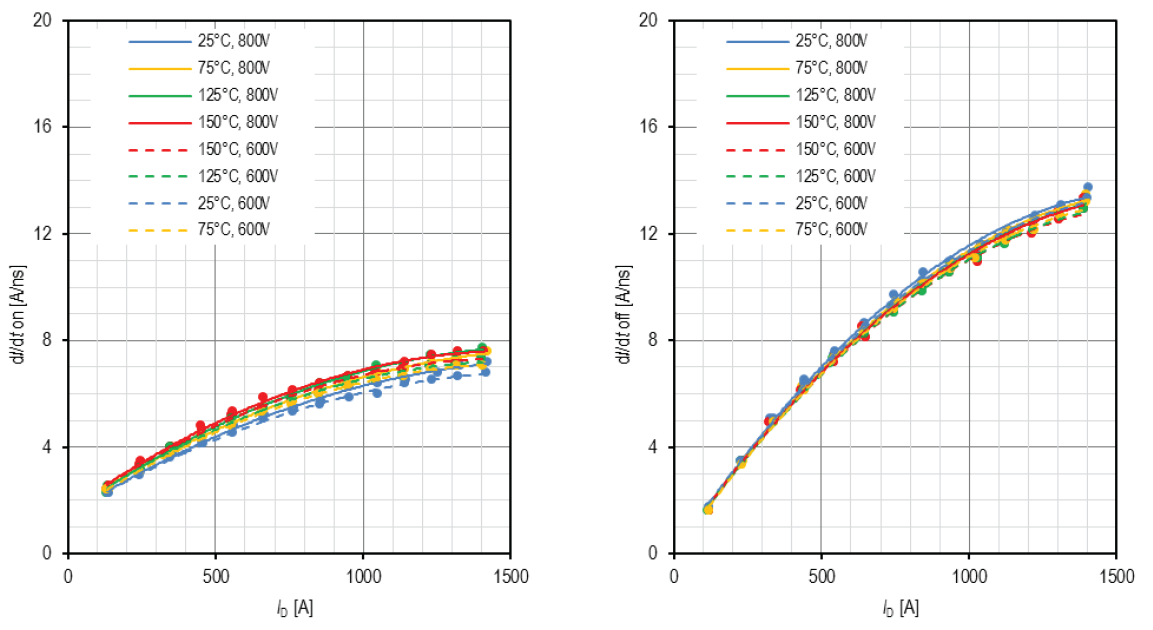
Figure 6: Turn-on di/dt versus ID / Figure 7: Turn-off di/dt versus ID
Two comments can be derived from Figure 6 and 7:
- The current slopes at turn–on and turn-off don’t show a strong dependency on chip temperature TJ and DC-link voltage VCC. This behavior differs from today’s IGBT-modules.
- The maximum di/dt at turning-off ID=1400A was about 13A/ns, which is quite similar to the switching speed known from today’s high current 1200V IGBT-modules.
Loss comparison with Si-based IGBT modules
The typical forward characteristics of new 800A full SiC module and existing 800A Si-based IGBT module are compared in Figure 8.
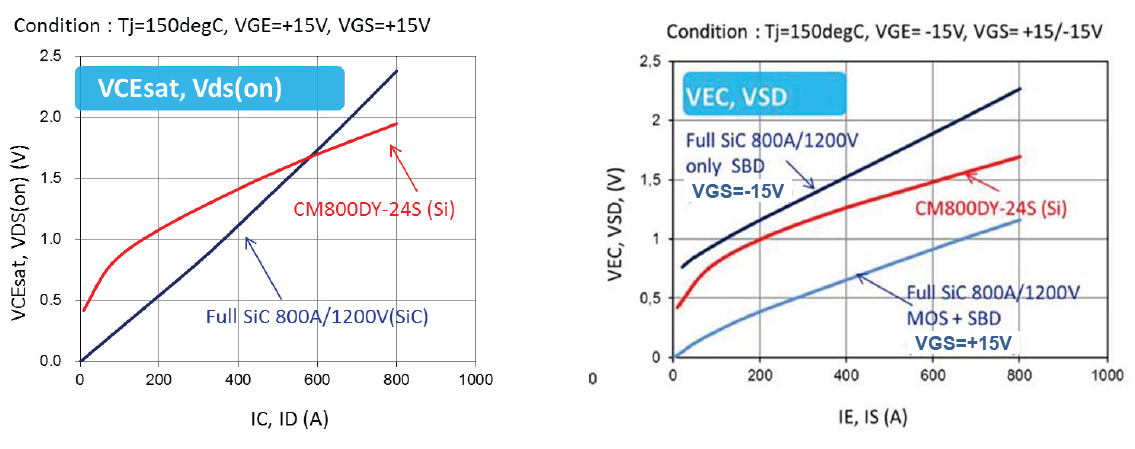
Figure 8: Forward characteristics
The comparison of switching energies in Figure 9 is indicating a key benefit of SiC technology: the switching losses can be drastically reduced compared with Si-based IGBT modules.
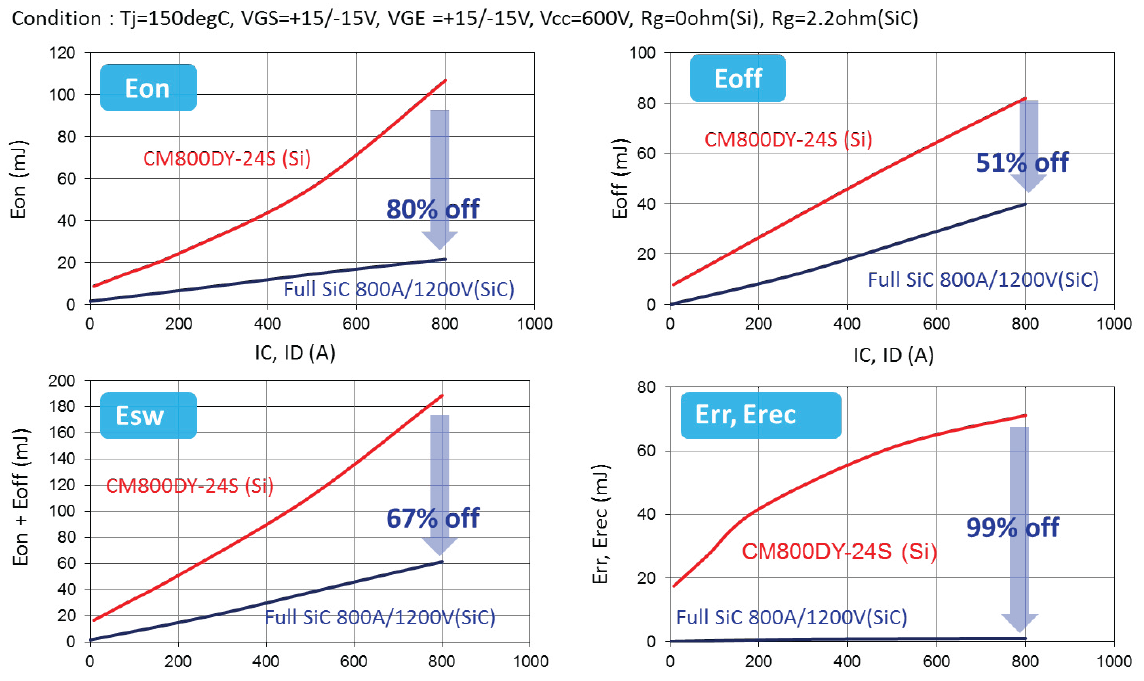
Figure 9: Switching energy comparison
This benefit can be seen in the power loss simulation results per Transistor/ FWDi-pair in inverter operation for two different PWM frequencies 15kHz and 30kHz and the corresponding temperature rise ΔT(j-c) in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
The total power loss can be drastically reduced (by 71% for 15kHz and 76% for 30kHz ) when full SiC-module is used. This loss reduction is mainly due to reduced switching loss. Conclusion: full SiC modules are very well suited for applications requiring high switching frequencies, where conventional Si-IGBT modules are reaching their thermal limit.
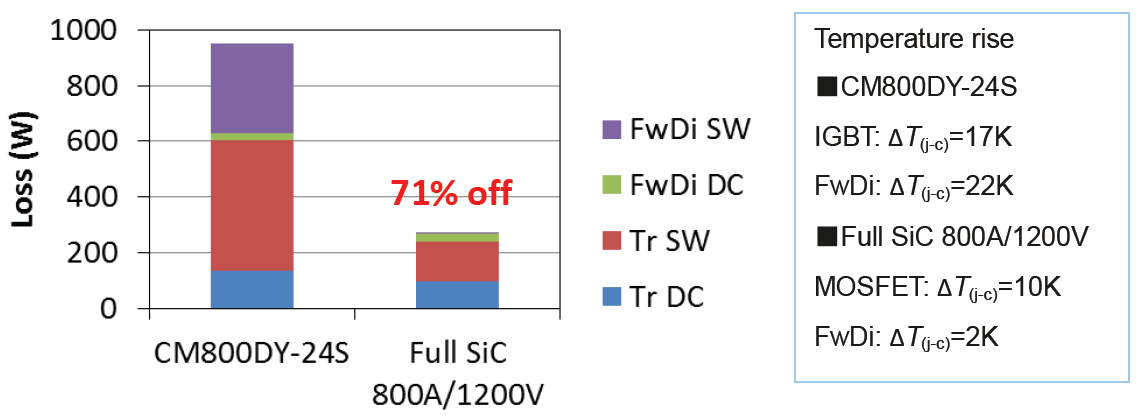
Figure 10: Loss and ΔT(j-c) simulation at fc=15kHz; VCC=600V; IO=400A(peak); PF=0,8; M=1,0
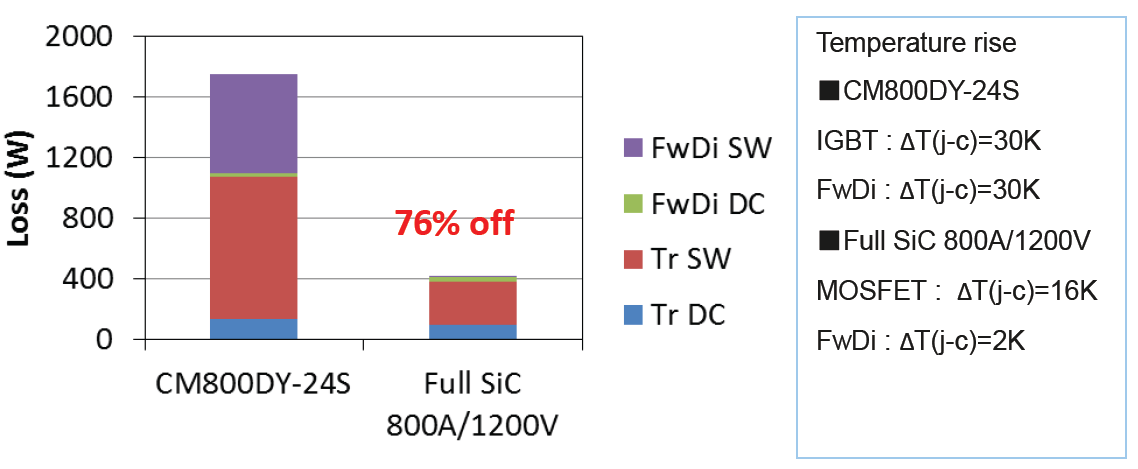
Figure 11: Loss and ΔT(j-c) simulation at fc=30kHz; VCC=600V; IO=400A(peak); PF=0,8; M=1,0
Gate Driver with SC-protection
The new 800A/1200V full SiC-Module can withstand a short circuit current for a limited time of tSC(max)=2,5μs. This limit is given in the SCSOA specification.
For conventional Si-IGBT modules typically a short circuit capability of tSC(max)=10μs is specified. In such conventional IGBT drivers a blanking time between desat-detection and SC-turn-off of typically to=1 3μs is installed, which is sufficient to ensure both: no false SC protection tripping and safe SC-turn-off.
Considering the relatively short tSC(max)=2,5μs specified for the new 800A/1200V full SiC-module another SC-protection method is proposed, known as RTC (Real Time Current Control). For this purpose one p-side and one n-side SiC MOSFET chip are equipped with a current sense electrode (refer to Figure 2). The equivalent circuit and the external view of this SiC MOSFET chip are shown in Figure 12.
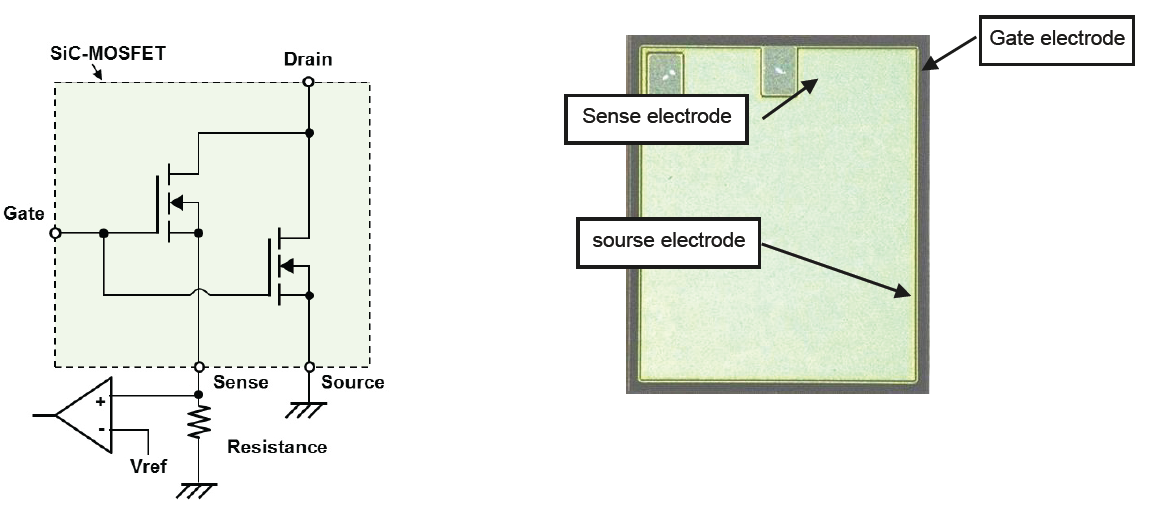
Figure 12: SiC MOSFET chip with current sense terminal
The functional block diagram of a dedicated gate driver for FMF800DX-24A using the proposed RTC protection is given in Figure 13. The measured short circuit waveforms during RTC operation are shown in Figure 14.
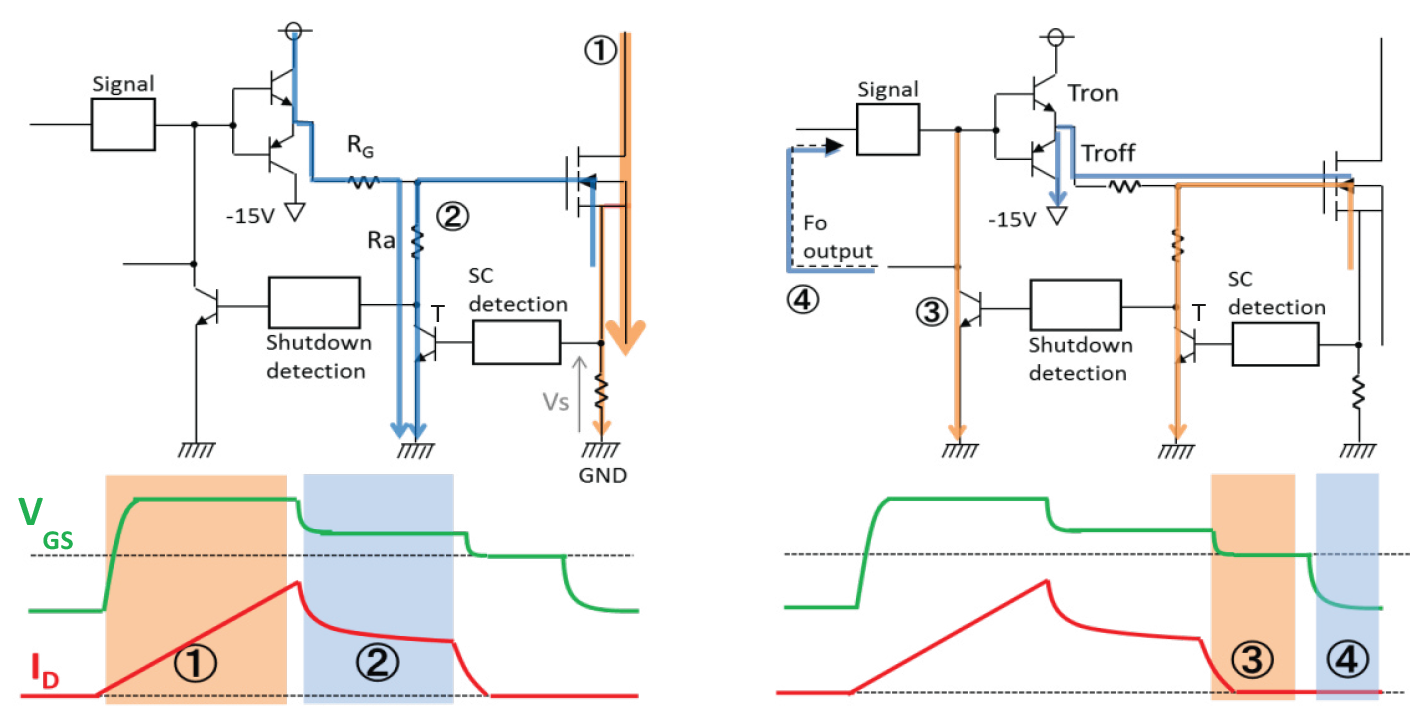
Figure 13: Principle of SC-protection by RTC
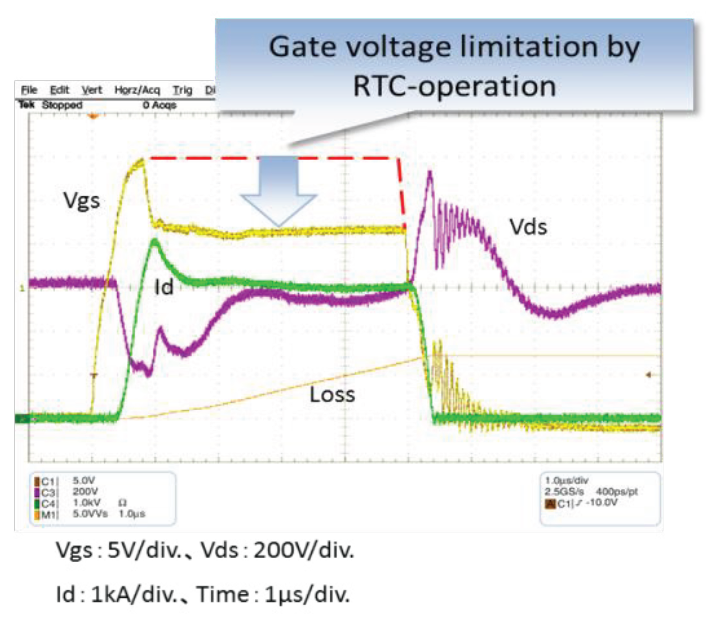
Figure 14: SC-waveforms during RTC-operation
During SC-turn-off operation by RTC four modes can be distinguished. In mode ① the main current ID is increasing until the voltage Vs across the shunt resistance is reaching a defined trip level. After reaching this trip level the mode ② starts: the transistor T is turned on and the Gate-Source voltage is reduced from +15V to about +7V resulting in a decreased SC-saturation current. Due to this SC-current reduction the allowable short circuit time is increased again to the well-known from IGBT drivers tsc(max)=10μs. Means from now on the conventional IGBT gate driver timing can be applied. During phase ③ the gate driver transistor Tron is switched off and VGS becomes Zero thus causing a soft turn-off of the short circuit current. In the final phase ④ the driver transistor Troff is turned on thus applying a negative VGS to the SiC MOSFET in off-state.
Summary and outlook
This paper is describing a new 800A/1200V full SiC dual module. Its type name is FMF800DX-24A. Compared with conventional Si-based IGBT modules the following unique points are confirmed:
- Module size reduced by 50%
- Switching loss (Esw=Eon + Eoff + Err) reduced by 75%
- Reliable SC-protection by RTC
Based on these features the new 800A/1200V full SiC module provides an interesting alternative to conventional IGBT modules in power electronic systems up to several 100kW, especially if one of the following system characteristics is of specific importance:
- Compact equipment size/high power density
- High efficiency
- High switching frequency (beyond the today’s limit reachable with IGBT modules)
References
[1]Press release No.2687 “Mitsubishi Electric to begin shipment of Silicon Carbide Power Modules Samples”, Tokyo, July 9, 2012
[2] Press release No.2733 “Mitsubishi Electric develops Large capacity SiC Power Module Technologies” Tokyo, February 14, 2013
Related posts
 Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
Now available – DC/DC converters from PREMIUM
 New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers
New release in DACPOL lighting for lathes – Kira covers




Leave a comment