

Category


Photos are for informational purposes only. View product specification
please use latin characters
What is an explosion hazard zone?
EXPLOSION HAZARD ZONE – a space in which a mixture of flammable substances with air or other oxidizing gases may occur, with a concentration between the lower and upper explosive limits.
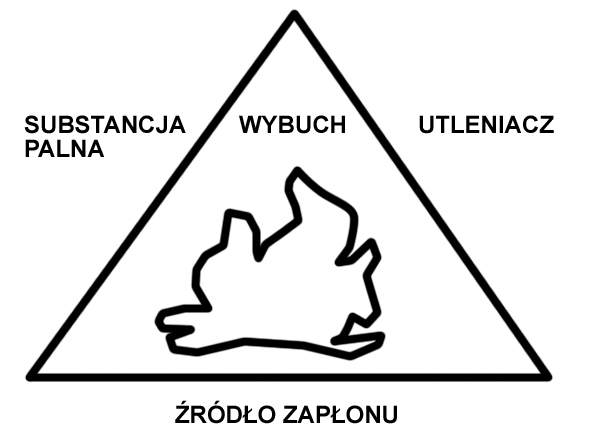
Flammable Properties:
- Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) is the lowest fuel concentration in a flammable mixture below which ignition of the mixture by an initiating factor and further spontaneous flame propagation under specific test conditions are not possible.
- Upper Explosive Limit (UEL) is the highest fuel concentration in a flammable mixture above which ignition of the mixture by an initiating factor and further spontaneous flame propagation under specific test conditions are not possible.
- Autoignition Temperature
| GAS | % GAS IN THE AIR | |
|---|---|---|
| DGW | GGW | |
| Hydrogen | 4.1 | 74.2 |
| Carbon Monoxide | 12.5 | 74.2 |
| Methane | 5.3 | 14.0 |
| Ethane | 3,2 | 12.5 |
| Propane | 2.4 | 9.5 |
| Butane | 1.9 | 8.4 |
| Acetylene | 2.5 | 80.00 |
| Gas | 5,6 | 31.00 |
| Water gas | 6.2 | 72.00 |
| Natural Gas | 4.5 | 17.00 |
| Mineral gas | 32 | 74.00 |

Autoignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a flammable substance ignites upon contact with a hot surface or as a result of thermal radiation from that surface (without the participation of an external flame or spark).
Gases and liquid vapors with an auto-ignition temperature below 85 oC are considered auto-igniting at room temperature.
TEMPERATURE TABLE
| Auto-ignition temperature, oC | Temperature class | Substance example |
|---|---|---|
| > 450 | Tl | Hydrogen, carbon monoxide, ammonia |
| >300 - 450 | T2 | Acetylene, n-butane, ethylene oxide |
| >200 - 300 | T3 | N-octane, turpentine, acrolein |
| >135 - 200 | T4 | Acetaldehyde, diethyl ether |
| >100 - 135 | T5 | Carbon disulfide |
| >85 - 100 | T6 | Phosphine |
IGNITION ENERGY
An explosion requires ignition. For ignition to be possible, the so-called IGNITION ENERGY.
Minimum ignition energy, Emin is the lowest energy of a capacitor in an electrical circuit, the discharge of which causes ignition of the mixture and propagation of a flame under specific test conditions.
The minimum ignition energy value is a parameter that allows for the assessment of the explosion hazard posed by energy sources existing in the area under consideration.
IGNITION SOURCES
• Mechanically generated sparks
• Electrical sparks
• Electrostatic sparks
• Hot surfaces
MINIMUM IGNITION ENERGIES OF GAS-AIR MIXTURES
| Flammable substance | Emin, mJ | DEVICE GROUP |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon disulfide | 0.009 | II C |
| Hydrogen | 0.019 | II B |
| Acetylene | 0.019 | II B |
| Ethylene oxide | 0.060 | II B |
| Methanol | 0.140 | II B |
| ethyl ether | 0.190 | II B |
| Benzene | 0.200 | II B |
| Hexane | 0.240 | II B |
| Butane | 0.250 | II B |
| Methane | 0.280 | II A |
| Acetone | 0.600 | II A |
DIVISION OF EQUIPMENT
Group I: methane in underground mine workings
Group II: gas, mists, vapors
IIA – propane group (260 µJ)
(122 gases and vapors, e.g.: Acetone, methyl and ethyl alcohol, acetone)
IIB – ethylene group (95 µJ)
(27 gases and vapors, e.g., ethylene, hydrogen sulfide)
IIC – hydrogen group (18 µJ)
(4 gases: acetylene, hydrogen, hydrazine, carbon disulfide)
Group III: dust and other
IIIA – explosive flocs
IIIB – non-conductive dust
IIIC – conductive dust
EX CLASSIFICATION
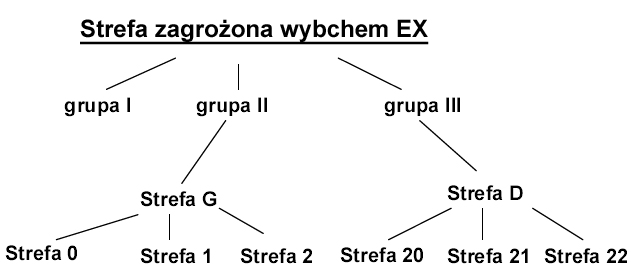
Zone G - Gases, mists, vapors
Zone D - dust
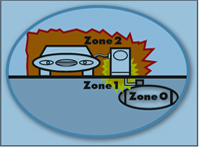
Zone 0 - an explosive atmosphere occurs continuously and persists for a long time
Zone 1 - an explosive atmosphere occurs sporadically
Zone 2 - an explosive atmosphere does not occur during normal operation, and if it does occur, it persists for a short time.
EQUIPMENT SAFETY CATEGORIES ACCORDING TO DIRECTIVE 94/9/EC
EQUIPMENT CATEGORY 1 - these devices provide a very high level of safety and allow for continuous operation where explosive atmospheres are constantly present => Zone "0"
DEVICE CATEGORY 2 - these devices provide a high level of protection => Zone "1"
DEVICE CATEGORY 3 - these devices provide a normal level of protection => Zone "2"
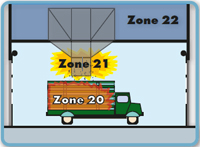
| Explosion Hazard Zone | Explosion Hazard Zone | Device Category |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 1 |
| 1 | 21 | 2 |
| 2 | 22 | 3 |
 |
 |
CE 0344 Ex II 2 G Ex e ia IIC T6
CE – quality declaration
0344 – identification number of the certification body
II – explosion group
2 – device category -> Zone 1, 21
G – gas hazard / D – dust hazard
Ex e ia – explosion protection type
IIC - explosion subgroup
T6 - temperature class – 85C
Classification of protection types:
d – flameproof construction according to IEC 60079-1, Polish standard PN-EN-50018:2000
ib – intrinsically safe construction according to IEC 60079-111, Polish standard PN-EN-50020:2000
e – reinforced construction according to IEC 60079-7, Polish standard PN-EN-50019:2000
q – with powder/sand shielding according to IEC 60079-5, Polish standard PN/E-08113 standard
n – devices intended for zone 2
k – waterproof
ia – intrinsically safe
p – with overpressure gas shield according to IEC 60079-2, Polish standard PN/E-08112
o – with oil shield according to IEC 60079-6, Polish standard PN/E-08114
m – hermetic enclosure
s – special version
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Control stations:
- polyester, stainless steel
- zones 1, 21
 |
 |
Junction and branch boxes:
- aluminum, Polyester, stainless steel
- zones 1, 21
 |
 |
Are you interested in this product? Do you need additional information or individual pricing?
What is an explosion hazard zone?
EXPLOSION HAZARD ZONE – a space in which a mixture of flammable substances with air or other oxidizing gases may occur, with a concentration between the lower and upper explosive limits.

Flammable Properties:
- Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) is the lowest fuel concentration in a flammable mixture below which ignition of the mixture by an initiating factor and further spontaneous flame propagation under specific test conditions are not possible.
- Upper Explosive Limit (UEL) is the highest fuel concentration in a flammable mixture above which ignition of the mixture by an initiating factor and further spontaneous flame propagation under specific test conditions are not possible.
- Autoignition Temperature
| GAS | % GAS IN THE AIR | |
|---|---|---|
| DGW | GGW | |
| Hydrogen | 4.1 | 74.2 |
| Carbon Monoxide | 12.5 | 74.2 |
| Methane | 5.3 | 14.0 |
| Ethane | 3,2 | 12.5 |
| Propane | 2.4 | 9.5 |
| Butane | 1.9 | 8.4 |
| Acetylene | 2.5 | 80.00 |
| Gas | 5,6 | 31.00 |
| Water gas | 6.2 | 72.00 |
| Natural Gas | 4.5 | 17.00 |
| Mineral gas | 32 | 74.00 |

Autoignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a flammable substance ignites upon contact with a hot surface or as a result of thermal radiation from that surface (without the participation of an external flame or spark).
Gases and liquid vapors with an auto-ignition temperature below 85 oC are considered auto-igniting at room temperature.
TEMPERATURE TABLE
| Auto-ignition temperature, oC | Temperature class | Substance example |
|---|---|---|
| > 450 | Tl | Hydrogen, carbon monoxide, ammonia |
| >300 - 450 | T2 | Acetylene, n-butane, ethylene oxide |
| >200 - 300 | T3 | N-octane, turpentine, acrolein |
| >135 - 200 | T4 | Acetaldehyde, diethyl ether |
| >100 - 135 | T5 | Carbon disulfide |
| >85 - 100 | T6 | Phosphine |
IGNITION ENERGY
An explosion requires ignition. For ignition to be possible, the so-called IGNITION ENERGY.
Minimum ignition energy, Emin is the lowest energy of a capacitor in an electrical circuit, the discharge of which causes ignition of the mixture and propagation of a flame under specific test conditions.
The minimum ignition energy value is a parameter that allows for the assessment of the explosion hazard posed by energy sources existing in the area under consideration.
IGNITION SOURCES
• Mechanically generated sparks
• Electrical sparks
• Electrostatic sparks
• Hot surfaces
MINIMUM IGNITION ENERGIES OF GAS-AIR MIXTURES
| Flammable substance | Emin, mJ | DEVICE GROUP |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon disulfide | 0.009 | II C |
| Hydrogen | 0.019 | II B |
| Acetylene | 0.019 | II B |
| Ethylene oxide | 0.060 | II B |
| Methanol | 0.140 | II B |
| ethyl ether | 0.190 | II B |
| Benzene | 0.200 | II B |
| Hexane | 0.240 | II B |
| Butane | 0.250 | II B |
| Methane | 0.280 | II A |
| Acetone | 0.600 | II A |
DIVISION OF EQUIPMENT
Group I: methane in underground mine workings
Group II: gas, mists, vapors
IIA – propane group (260 µJ)
(122 gases and vapors, e.g.: Acetone, methyl and ethyl alcohol, acetone)
IIB – ethylene group (95 µJ)
(27 gases and vapors, e.g., ethylene, hydrogen sulfide)
IIC – hydrogen group (18 µJ)
(4 gases: acetylene, hydrogen, hydrazine, carbon disulfide)
Group III: dust and other
IIIA – explosive flocs
IIIB – non-conductive dust
IIIC – conductive dust
EX CLASSIFICATION

Zone G - Gases, mists, vapors
Zone D - dust
Zone 0 - an explosive atmosphere occurs continuously and persists for a long time
Zone 1 - an explosive atmosphere occurs sporadically
Zone 2 - an explosive atmosphere does not occur during normal operation, and if it does occur, it persists for a short time.
EQUIPMENT SAFETY CATEGORIES ACCORDING TO DIRECTIVE 94/9/EC
EQUIPMENT CATEGORY 1 - these devices provide a very high level of safety and allow for continuous operation where explosive atmospheres are constantly present => Zone "0"
DEVICE CATEGORY 2 - these devices provide a high level of protection => Zone "1"
DEVICE CATEGORY 3 - these devices provide a normal level of protection => Zone "2"
| Explosion Hazard Zone | Explosion Hazard Zone | Device Category |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 1 |
| 1 | 21 | 2 |
| 2 | 22 | 3 |
 |
 |
CE 0344 Ex II 2 G Ex e ia IIC T6
CE – quality declaration
0344 – identification number of the certification body
II – explosion group
2 – device category -> Zone 1, 21
G – gas hazard / D – dust hazard
Ex e ia – explosion protection type
IIC - explosion subgroup
T6 - temperature class – 85C
Classification of protection types:
d – flameproof construction according to IEC 60079-1, Polish standard PN-EN-50018:2000
ib – intrinsically safe construction according to IEC 60079-111, Polish standard PN-EN-50020:2000
e – reinforced construction according to IEC 60079-7, Polish standard PN-EN-50019:2000
q – with powder/sand shielding according to IEC 60079-5, Polish standard PN/E-08113 standard
n – devices intended for zone 2
k – waterproof
ia – intrinsically safe
p – with overpressure gas shield according to IEC 60079-2, Polish standard PN/E-08112
o – with oil shield according to IEC 60079-6, Polish standard PN/E-08114
m – hermetic enclosure
s – special version
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Control stations:
- polyester, stainless steel
- zones 1, 21
 |
 |
Junction and branch boxes:
- aluminum, Polyester, stainless steel
- zones 1, 21
 |
 |
Your review appreciation cannot be sent
Report comment
Report sent
Your report cannot be sent
Write your review
Review sent
Your review cannot be sent
