-
BackX
-
Components
-
-
Category
-
Semiconductors
- Diodes
- Thyristors
-
Electro-insulated Modules
- Electro-insulated Modules | VISHAY (IR)
- Electro-insulated Modules | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Electro-insulated Modules | Semikron
- Electro-insulated Modules | POWEREX
- Electro-insulated Modules | IXYS
- Electro-insulated Modules | POSEICO
- Electro-insulated Modules | ABB
- Electro-insulated Modules | TECHSEM
- Go to the subcategory
- Bridge Rectifiers
-
Transistors
- Transistors | GeneSiC
- SiC MOSFET Modules | Mitsubishi
- SiC MOSFET Modules | STARPOWER
- Module SiC MOSFET ABB’s
- IGBT Modules | MITSUBISHI
- Transistor Modules | MITSUBISHI
- MOSFET Modules | MITSUBISHI
- Transistor Modules | ABB
- IGBT Modules | POWEREX
- IGBT Modules | INFINEON (EUPEC)
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) semiconductor elements
- Go to the subcategory
- Gate Drivers
- Power Blocks
- Go to the subcategory
- Electrical Transducers
-
Passive components (capacitors, resistors, fuses, filters)
- Resistors
-
Fuses
- Miniature Fuses for electronic circuits - ABC & AGC Series
- Tubular Fast-acting Fuses
- Time-delay Fuse Links with GL/GG & AM characteristics
- Ultrafast Fuse Links
- Fast-acting Fuses (British & American standard)
- Fast-acting Fuses (European standard)
- Traction Fuses
- High-voltage Fuse Links
- Go to the subcategory
- Capacitors
- EMI Filters
- Supercapacitors
- Power surge protection
- TEMPEST emission revealing filters
- Surge arrester
- Go to the subcategory
-
Relays and Contactors
- Relays and Contactors - Theory
- 3-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays
- DC Semiconductor Relays
- Controllers, Control Systems and Accessories
- Soft Starters and Reversible Relays
- Electromechanical Relays
- Contactors
- Rotary Switches
-
Single-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays
- AC ONE PHASE RELAYS 1 series| D2425 | D2450
- One phase semiconductor AC relays CWA and CWD series
- One phase semiconductor AC relays CMRA and CMRD series
- One phase semiconductor AC relays - PS series
- Double and quadruple semiconductor AC relays - D24 D, TD24 Q, H12D48 D series
- One phase semiconductor relays - gn series
- Ckr series single phase solid state relays
- One phase AC semiconductor relays for DIN bus - ERDA I ERAA series
- 150A AC single phase relays
- Rail Mountable Solid State Relays With Integrated Heat Sink - ENDA, ERDA1 / ERAA1 series
- Go to the subcategory
- Single-Phase AC Semiconductor Relays for PCBs
- Interface Relays
- Go to the subcategory
- Cores and Other Inductive Components
- Heatsinks, Varistors, Thermal Protection
- Fans
- Air Conditioning, Accessories for Electrical Cabinets, Coolers
-
Batteries, Chargers, Buffer Power Supplies and Inverters
- Batteries, Chargers - Theoretical Description
- Modular Li-ion Battery Building Blocks, Custom Batteries, BMS
- Batteries
- Battery Chargers and Accessories
- Uninterruptible Power Supply and Buffer Power Supplies
- Inverters and Photovoltaic Equipments
- Energy storage
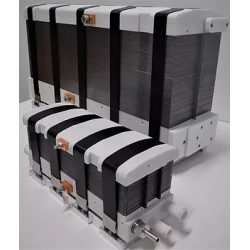
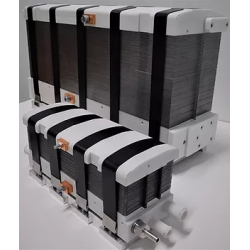
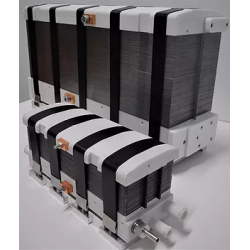
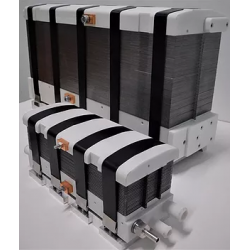
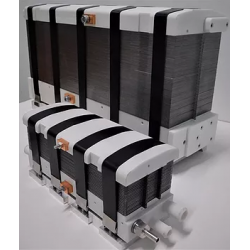
- Fuel cells
- Lithium-ion batteries
- Go to the subcategory
-
Automatics
- Spiralift Lifts
- Futaba Drone Parts
- Limit Switches, Microswitches
- Sensors, Transducers
-
Infrared Thermometers (Pyrometers)
- IR-TE Series - Water-proof Palm-sized Radiation Thermometer
- IR-TA Series - Handheld Type Radiation Thermometer
- IR-H Series - Handheld Type Radiation Thermometer
- IR-BA Series - High-speed Compact Radiation Thermometer
- IR-FA Series - Fiber Optic Radiation Thermometer
- IR-BZ Series - Compact Infrared Thermometers
- Go to the subcategory
- Counters, Time Relays, Panel Meters
- Industrial Protection Devices
- Light and Sound Signalling
- Thermographic Camera
- LED Displays
- Control Equipments
- Go to the subcategory
-
Cables, Litz wires, Conduits, Flexible connections
- Wires
- Cable feedthroughs and couplers
- Litz wires
-
Cables for extreme applications
- Extension and Compensation cables
- Thermocouple cables
- Connection cables for PT sensors
- Multi-conductor wires (temp. -60C to +1400C)
- Medium voltage cables
- Ignition wires
- Heating cables
- Single conductor cables (temp. -60C to +450C)
- Railway cables
- Heating cables Ex
- Cables for the defense industry
- Go to the subcategory
- Sleevings
-
Braids
- Flat Braids
- Round Braids
- Very Flexible Flat Braids
- Very Flexible Round Braids
- Cylindrical Cooper Braids
- Cylindrical Cooper Braids and Sleevings
- Flexible Earthing Connections
- PCV Insulated Copper Braids (temp. up to 85C)
- Flat Aluminium Braids
- Junction Set - Braids and Tubes
- Steel Braids
- Go to the subcategory
- Traction Equipment
- Cable Terminals
- Flexible Insulated Busbars
- Flexible Multilayer Busbars
- Cable Duct Systems
- Go to the subcategory
- View all categories
-
Semiconductors
-
-
- Suppliers
-
Applications
- CNC Machine Tools
- DC and AC Drives (Inverters)
- Energetics
- Energy bank
- Equipment and Components for Hazardous Areas [Ex]
- Equipment for Distribution, Control and Telecommunications Cabinets
- HVAC Automation
- Induction Heating
- Industrial Automation
- Industrial Protective Devices
- Machines for Drying and Wood Processing
- Machines for Thermoforming Plastics
- Mining, Metallurgy and Foundry
- Motors and Transformers
- Power Supplies (UPS) and Rectifier Systems
- Printing
- Temperature Measurement and Regulation
- Test and Laboratory Measurements
- Tram and Railway Traction
- Welding Machines
-
Assembly
-
-
Inductors
-
-
Induction devices
-
-
Service
-
- Contact
- Zobacz wszystkie kategorie
Hydrogen Fuel Cells – Applications

Hydrogen fuel cells are a modern technology that is gaining increasing importance in energy and automotive sectors. Hydrogen cells allow the conversion of chemical energy from hydrogen directly into electrical energy, with minimal emission of harmful substances. As a result, they are becoming one of the most promising sources of clean energy, with the potential to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and support the energy transition toward sustainable development.
Principle of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells are based on a simple yet efficient electrochemical process. In a classic PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) cell, hydrogen is supplied to the anode, where it undergoes oxidation. Protons pass through the polymer membrane to the cathode, while electrons flow through an external circuit, generating electric current. At the cathode, hydrogen reacts with oxygen from the air, producing water – the only byproduct.
This process makes hydrogen fuel cells not only efficient but also environmentally friendly. Compared to traditional internal combustion engines, hydrogen fuel cells generate energy without emitting harmful greenhouse gases. In practice, this means that electric vehicles using this technology can operate directly on pure hydrogen, with water vapor as their only byproduct.
Types and Construction of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
The most common hydrogen fuel cells are PEM cells, but on an industrial scale, alkaline, solid oxide, and phosphoric acid cells are also used. Depending on the application, they differ in operating temperature, energy density, and type of electrolyte.
Key components of every hydrogen fuel cell include:
- Anode and cathode – electrodes where chemical reactions occur, often coated with a platinum catalyst.
- Polymer membrane – enables proton exchange between the anode and cathode.
- External circuit – conducts the electrons generated during hydrogen oxidation.
Thanks to this design, it is possible to generate electrical energy continuously and steadily, without the need for combustion-based energy sources.
Applications of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Automotive
The most recognized application of hydrogen fuel cells is in the automotive sector. Hydrogen-powered vehicles offer similar comfort to electric cars, but with the advantages of fast refueling and longer range. Hydrogen can be stored in pressurized tanks, and fuel cells generate energy on demand, eliminating the need for large batteries.
Industry and Energy
Hydrogen fuel cells are also used for electricity generation, including in emergency power stations, microgrids, and energy storage systems. When combined with renewable energy sources such as wind or solar, they allow excess energy to be stored as hydrogen and recovered during periods of high demand.
Portable Power Sources
Hydrogen fuel cells are also used in portable electronic devices and off-grid power systems. Their advantages include compactness, long lifespan, and zero carbon dioxide emissions. They can power drones, industrial robots, and even rescue equipment in locations without access to a conventional power grid.
Production Process and Technological Challenges
The production of fuel cells requires precise technology and high-quality materials, especially polymer membranes and catalysts. Producing hydrogen in a clean and efficient way remains a key challenge – methods include methane reforming, water electrolysis, and natural gas utilization. Each method has its pros and cons, and the choice affects the cost and environmental impact of the entire system.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High energy efficiency and process cleanliness – the only byproduct is water.
- Fast refueling and long range in hydrogen vehicles.
- Versatile applications – from automotive to industry and energy.
- Ability to integrate with renewable energy sources.
Disadvantages:
- High cost of membrane and catalyst production.
- Difficulties in storing and distributing hydrogen.
- Sensitivity to gas contaminants, which can weaken cell performance.
Despite these challenges, the development of hydrogen fuel cell technology is progressing rapidly. As hydrogen production costs decrease and materials improve, their use will become increasingly widespread.
The Future of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells fit into the global energy transition. They make it possible to reduce CO₂ emissions, replace fossil fuels, and introduce sustainable energy sources. Growing interest in hydrogen-powered vehicles, energy storage, and industrial-scale electricity production shows that fuel cells have the potential to become one of the key energy sources in the coming decades.
The scalability of the technology, its ability to operate in diverse conditions, and minimal environmental impact make hydrogen fuel cells a promising solution for industry, energy, and transport. Integrating hydrogen cells with other renewable energy sources further increases their value, enabling the creation of more resilient and eco-friendly energy systems.
Hydrogen fuel cells offer broad applications and a real opportunity to change how energy is produced and used. This technology not only increases energy efficiency but also significantly reduces environmental impact.
We invite you to explore our offerings. We provide a wide range of hydrogen solutions that can be tailored to industrial needs.
Related products
Related posts
 Thermally conductive materials in power storages
Thermally conductive materials in power storages
 Measuring power and energy in electric circuits
Measuring power and energy in electric circuits
 Wentylatory przemysłowe - rodzaje, właściwości
Wentylatory przemysłowe - rodzaje, właściwości









Leave a comment