Shielding
Categories
- Conductive adhesives, paints
- Spiral gaskets
- Form-In-Place Electrically Conductive Cast Gaskets
- EMC products for PCB
- EMC coatings of plastic surfaces
- Microwave absorbers / EMC shielding mats
- EPDM edge seals
- Conductive tapes
- Window screening
- Shielding of ventilation openings
- Shielding components on PCBs
- EMC seals and contact pads
- Theory – Electromagnetic Protection Products
- Woven mesh seals
- Foam seals
- EMC conductive elastomers
Shielding: Comprehensive Strategies for EMC Protection in Modern Electronics
In today's world, saturated with electromagnetic signals, effective Shielding is absolutely crucial to ensuring the reliability and compliance with Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) standards of every electronic device. Shielding is the process of creating barriers that prevent the emission of interference outside the device (emission) and protect it from interference originating from the environment (susceptibility). Research and Development (R&D) departments face the challenge of selecting the most effective and economical solutions, which often combine advanced chemistry and precise mechanical engineering. Below is an overview of key shielding products and methods.
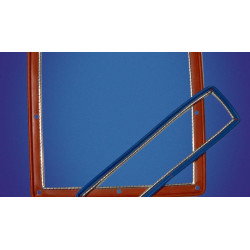
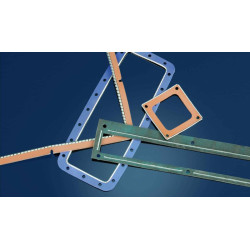
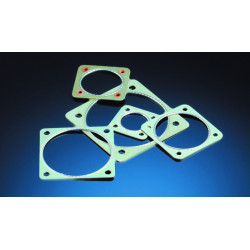
Securing critical gaps: EMC Gaskets and seals
Even the best-designed enclosure becomes useless if it has leaks that allow the escape or penetration of electromagnetic interference. To prevent this, a range of specialized seals are used. Foam gaskets and EPDM edge gaskets with conductive fillings provide excellent mechanical and electrical connection on doors, panels, and covers. Where extreme performance and durability are required, Coil gaskets or Knitted mesh gaskets are used, often employed for shielding in demanding military and aerospace applications. An innovative method is the use of Dispensed electrically conductive Form-In-Place gaskets, which are automatically applied, creating a precise, conductive seal directly on the enclosure. Additionally, EMC gaskets and contact pads are indispensable for creating localized, low-resistance connections between components.
Shielding surfaces and components
To impart shielding properties to plastic enclosures, which are non-conductive themselves, EMC coatings for plastic surfaces are used. These are conductive paints and lacquers that create a continuous shielding layer. For the protection of the circuits themselves, EMC products for PCB boards are necessary. These include miniature shields, pastes, and grounding elements that ensure Shielding of elements on PCB boards, minimizing crosstalk and local interference. In cases where interference is already generated but needs to be suppressed, Microwave absorbers / EMC shielding mats are utilized. These materials, often containing Conductive EMC elastomers, absorb electromagnetic energy instead of reflecting it, which is crucial in resonant spaces and for suppressing internal noise.
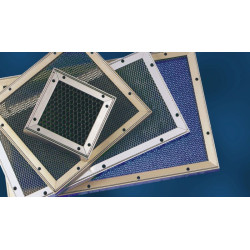
Solutions for interfaces and critical access points
A specific challenge in Shielding is the necessity to maintain the functionality of interfaces and openings. For the protection of displays and indicators, Window shielding – transparent conductive films or meshes – is used. To ensure air exchange without losing shielding effectiveness, Shielding of ventilation openings using special honeycomb panels is required. Conductive tapes, which are flexible and easy to apply, are used for quickly creating connections and repairs. Ensuring the continuity of grounding and shielding at these critical points is a priority in R&D projects, as even small apertures can drastically reduce the effectiveness of the entire EMC system.